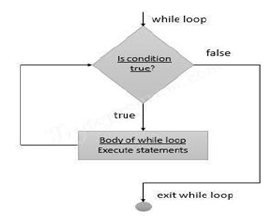
A repetition structure causes a statement or set of statements to execute repeatedly. Repetition structure, which is more commonly known as a loop is used to repeat a set of statements.
Two broad categories of
loops are: condition-controlled and count-controlled.
A condition-controlled
loop uses a true/false condition to control the number of times that it repeats.
A count-controlled
loop repeats a specific number of times.
In Python the while
statement is used to write a condition-controlled loop, and the for statement is
used to write a count-controlled loop.
1. While loop:
- Loops are either infinite or conditional. Python while loop keeps reiterating a block of code defined inside it until the desired condition is met.
- The while loop contains a boolean expression and the code inside the loop is repeatedly executed as long as the boolean expression is true.
- The statements that are executed inside while can be a single line of code or a block of multiple statements.
Syntax:
while(expression):
Statement(s)
Example:
i=1
while i<=6:
print("TTWRDC")
i=i+1
2. For loop:
Python for loop is
used for repeated execution of a group of statements for the desired number of
times. It iterates over the items of lists, tuples, strings, the dictionaries
and other iterable objects.
Syntax:
for var in sequence:
Statement(s)
Example 1:
numbers = [1, 2, 4, 6,
11, 20]
seq=0
for val in numbers:
seq=val*val
print(seq)
Example 2: Iterating
over a Tuple:
tuple = (2,3,5,7)
print ('These are the
first four prime numbers ')
#Iterating over the tuple
for a in tuple:
print
(a)
Example 3: Iterating
over a dictionary:
#creating a dictionary
college =
{"MPCs":"block1","BZC":"block2","BCom":"block3"}
#Iterating over the
dictionary to print keys
print ('Keys are:')
for keys in college:
print
(keys)
#Iterating over the
dictionary to print values
print ('Values are:')
for blocks in college.values():
print(blocks)
Example 4: Iterating
over a String:
#declare a string to
iterate over
college = 'TTWRDC'
#Iterating over the
string
for name in college:
print
(name)
3. Nested For loop:
When one Loop defined
within another Loop is called Nested Loops.
Syntax:
for val in sequence:
for
val in sequence:
statements
statements
Example:
for i in range(1,6):
for
j in range(0,i):
print(i,
end=" ")